Key Visualizations in This Part
-
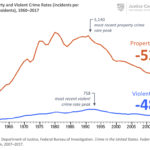
National property and violent crime rates have dropped 50 percent since their…
-
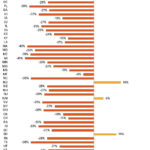
All but four states have experienced a decline in the property crime…
-

Violent crime rates increased in 19 states between 2007 and 2017, and…
-

In 16 states, violent crime rates decreased overall, but increased in areas…
-
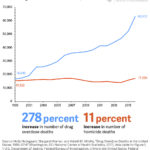
The number of drug overdose deaths used to mirror the number of…
The public safety pressures state and local governments face today are dramatically different than they were just 10 or 20 years ago.
Local communities are facing increasing challenges related to the large number of people who have mental illnesses who cycle through jails and emergency rooms and the high number of overdoses due to the opioid epidemic and other drugs. Jails are increasingly overcrowded, and trust in law enforcement and the criminal justice system has been damaged by highly-publicized officer-involved shootings.
These acute local challenges have coincided with a recent uptick in the national violent crime rate following two decades where the violent crime rate dropped 50 percent.[1] Not all state and local crime trends have mirrored national trends, however. While some states and cities are facing a pronounced increase in crime, others continue to experience declines.[2]
Successfully managing the changing criminal justice landscape requires state and local leaders to adopt innovative approaches based on data and research on what works to reduce crime and strengthen communities.
Key Strategies for Success
States have pursued four key strategies to support local jurisdictions as they adopt innovative approaches to fight crime, respond to people who have behavioral health needs, reduce overcrowding in jails, and support improvements to policing practices:
- Strategy 1: Use data to understand crime trends.
- Strategy 2: Improve responses to people who have behavioral health needs in local criminal justice systems.
- Strategy 3: Help local governments use jail space cost effectively.
- Strategy 4: Develop crime-reduction strategies that prevent violent crime and strengthen trust in law enforcement.
U.S. Department of Justice, Federal Bureau of Investigation, “Crime in the United States” (Washington, DC: U.S. Department of Justice, 2006–2016).
Ibid.
